

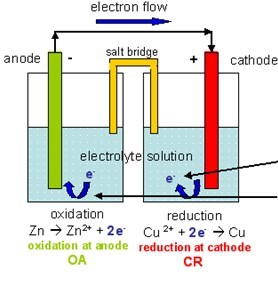
Let P 4 be taken in excess and allow to react it with Cl 2, then PCl 3 is formed in which P has +3 oxidation state. Third illustration P 4 is a reducing agent while Cl 2 is an oxidising agent. The Anode is the negative or reducing electrode that releases electrons to the external circuit and oxidizes during and electrochemical reaction. On the other hand, let O 2 be taken in excess, then Na 2 O 2 is formed in which has -1 oxidation state which is higher than -2. Write the anode and cathode reactions and the overall reaction occuring in a lead storage battery. Copper is used for the electrode on the right (the Cathode) in contact with. Sodium oxide (Na 2 O) is formed in which oxygen has -2 oxidation state. The battery operates through electrochemical reactions called oxidation and. Let sodium be taken in excess and allowed to burn in a limited supply of O 2. Na/Na+ in NASICON-type Na2CrTi(PO4)3 (NCTP). Here we report a reversible Cr4+/Cr3+ redox reaction at 4.5 V vs. In any electrochemical cell, the electrons always move from anode to cathode. The development of high-voltage cathode materials composed of abundant metals for rechargeable batteries is a crucial task to realize higher energy density in large-scale electrical energy storage systems. Here, we report a nitroaromatic cathode that performs a six-electron reaction per nitro group, drastically improving the specific capacity and energy density. Sodium is a reducing agent while oxygen is an oxidising agent. Galvanic cells always involve spontanous oxidation-reduction reactions. CO has formed in which carbon has +2 oxidation state (lower oxidation state).Īlso, let O 2 be taken in excess, then initially formed CO gets oxidised to CO 2 in which carbon has +4 oxidation state (higher oxidation state). The Fact given in the question is clear from the following illustration.įirst illustration: Carbon is a reducing agent while oxygen is an oxidising agent Let carbon be taken in excess and allowed to burn in a limited supply of O 2. The cathode supplies electrons to the positively charged cations which flow to it from the electrolyte (even if the cell is galvanic, i.e., when the cathode is positive and therefore would be expected to repel the positively charged cations this is due to electrode potential relative to the electrolyte solution being different for the anode and cathode metal/electrolyte systems in a galvanic cell).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
